Cardiac Sarcoidosis: The Rare Inflammatory Condition That Affects the Heart
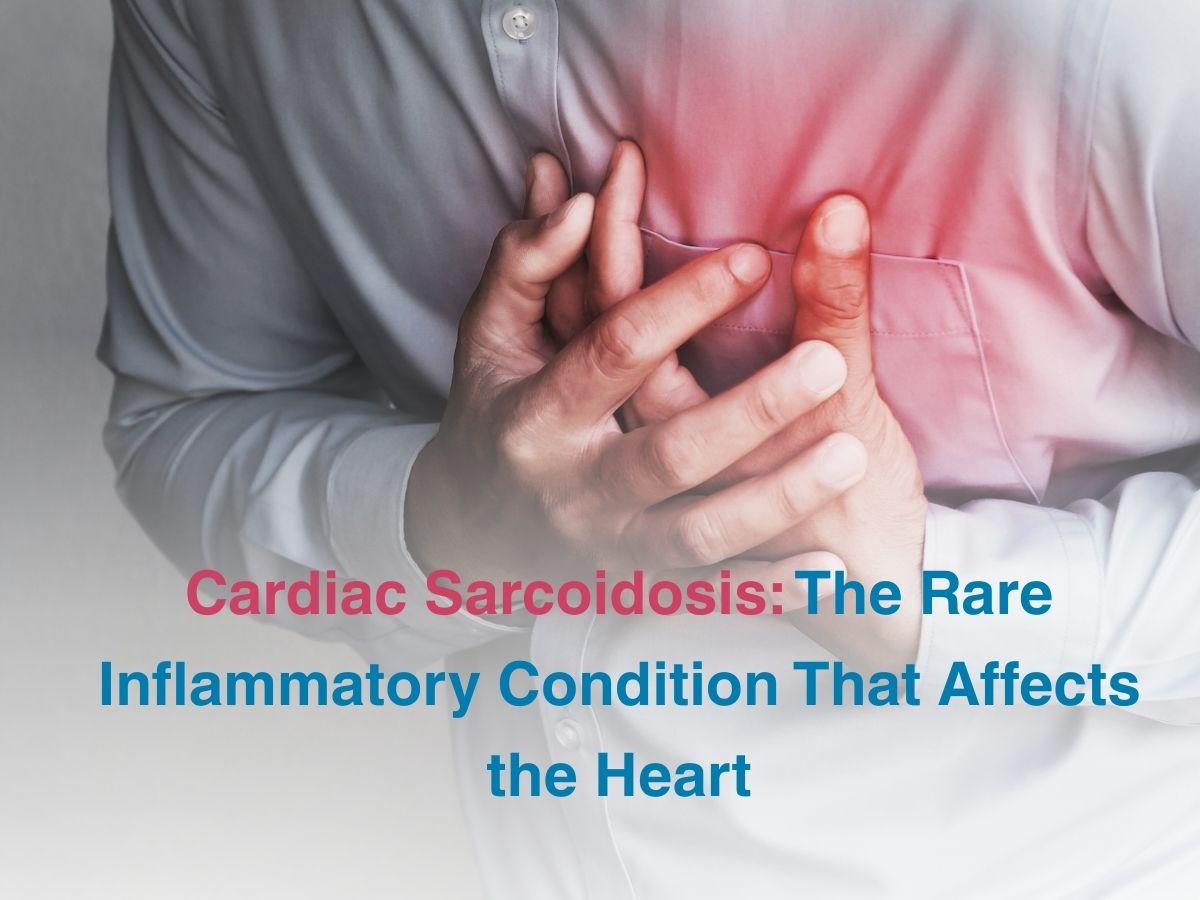
Cardiac sarcoidosis is a condition where inflammatory tissue called granulomas form inside the heart and negatively impact the way it can function. Heart muscles can get severely affected, leading to issues like arrhythmias and scarring. Sarcoidosis is an autoimmune disorder that is characterised by the formation of inflammatory sarcoids in the lungs and other parts of the body. When the heart gets affected too, it can cause various symptoms that mimic a heart attack or palpitations. In India, about 15% of sarcoidosis cases have a cardiac component to them, though the actual numbers may be higher or lower. Studies have shown that sarcoidosis is hard to diagnose in a timely fashion as the symptoms mimic that of tuberculosis.
Cardiac Sarcoid Symptoms
Some common symptoms of cardiac sarcoidosis are as follows
- Having to deal with chest pain or tightness
- Feeling faint and coughing a lot
- Shortness of breath is a common sign
- Swelling in the limbs or extremities is common too
- Some people report heat palpitations.
Heart Block Causes
Studies have not shown a particular reason for some people getting sarcoidosis while others remain healthy. But, researchers think that it may be due to mutated genes that cause the immune system to work too hard and cause sarcoids or granulomas in the heart, lungs and other parts of the body.
Diagnosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis
Apart from a physical exam, your doctor may recommend a series of tests that are designed to check how your heart is working and also to visualise for any structural abnormalities. Tests like blood tests, x-rays and EKG or ECG can help your doctor understand how well your heart is functioning. A cardiac MRI for sarcoidosis is a standard test done to see where inflammation and scar tissue formation is present – if the individual comes back repeatedly with pericardial effusion with unknown origins. Rarely, you may be asked to get an endomyocardial biopsy- but these are not highly sensitive. However, a biopsy is a confirmatory gold standard test that is done in some cases.
Other tests are designed to continuously monitor your heart- like a holter monitor, or a heart PET scan. They check for cardiac muscle function, electrical circuitry in your heart and if there is any possibility of an arrhythmia making things worse.
Treatment Of Cardiac Sarcoidosis
Since sarcoidosis is an autoimmune condition, steroids are commonly prescribed to modulate immune response and reduce inflammation. Immunosuppressants may be recommended at times, along with steroids. Antiarrhythmic drugs are given if you have arrhythmias while ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers are prescribed if you have early stage heart failure.
If conventional treatments don’t work, then surgery may be the only resort left to try. Procedures like pacemaker insertion can help your heart beat better. An ICD can be used to improve cardiac rhythm while cardiac ablation or the destruction of the part of the heart’s circuitry or tissues that is causing the arrhythmias is done. The subsequent scar tissue that forms over the site of ablation or injury stops any unwanted symptoms from reoccurring.
Conclusion
Cardiac sarcoidosis is an autoimmune condition that is chronic and can affect cardiac function in the long run. If you notice worrisome symptoms like severe chest pain, an irregular pulse, feel faint or dizzy and have severe heart palpitations, it is better to rush for emergency care- as it can be fatal if not immediately dealt with. If cardiac sarcoidosis is untreated, complications like atrial or ventricular fibrillation can occur. You may also be at high risk of developing heart blocks, heart failure or even sudden cardiac death in extreme cases.