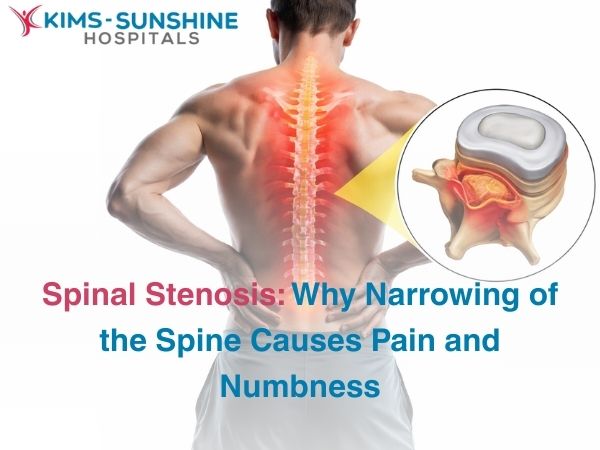
Spinal Stenosis: Why Narrowing of the Spine Causes Pain and Numbness
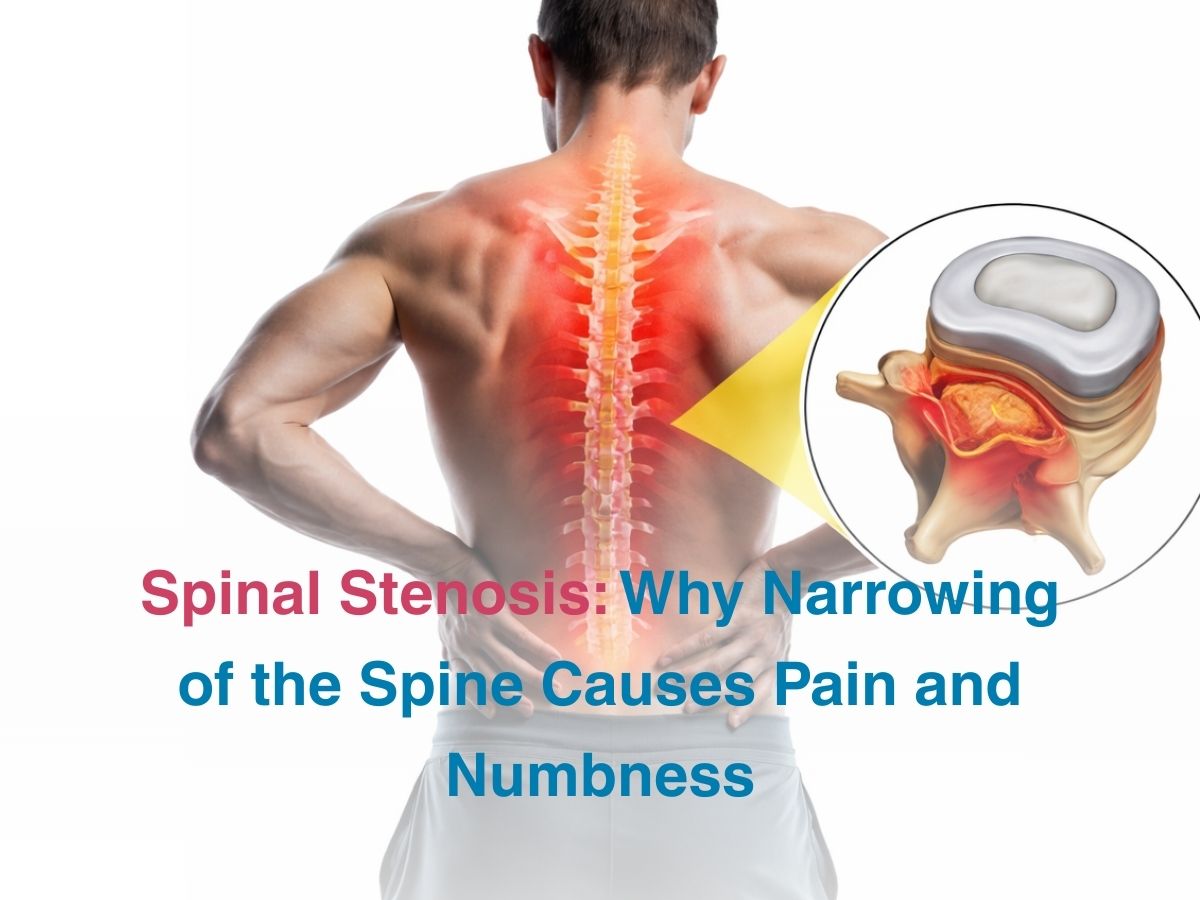
Stenosis is a condition that occurs when vessels or parts of body spaces shrink in size. When this happens in the spine, it can severely compress nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms that may be minor, severe or downright uncomfortable and painful. Many individuals with spinal stenosis don’t show any overt symptoms but for others- when it has progressed for too long, nerve compression symptoms begin to show up. Lumbar spinal stenosis occurs when the 5 bones in the lower back get worn down and nerves in that region get compressed. Cervical spinal stenosis on the other hand is caused when the cervical vertebrae in the neck get affected, leading to pain and related symptoms. Spinal stenosis is highly prevalent in the Indian population, with more older women getting affected than men.
Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
Some of the well known symptoms of this condition include
- Lower back pain or lumbago.
- Pain that begins in the bottom half of your body and radiates to the legs from the buttocks.
- Numbness, tingling or various sensations in the feet or buttocks.
- Pain that gets worse when you stand still or try to walk downhill.
- Pain that seems to get marginally better when you move uphill, sit or lean forward. These symptoms are associated with lumbar stenosis.
- Having issues with balance
- Having fine motor control problems- like not being able to write or button a top for example. It may also affect how you cook or go about your day gradually. This is more common with cervical stenosis.
For some people, spinal stenosis may be a congenital defect- which means they have narrower spinal spaces from birth. But most cases are acquired and may be due to injury, wear and tear, tumours or other issues.
Diagnosis of Spinal Stenosis
A detailed physical exam is one of the best ways to understand how severe your symptoms are- and this is when you will be asked to bend in different directions. Your symptoms may feel worse when you bend a certain way. Imaging tests allow your doctor to see the extent of damage in great detail.
- You can get a spinal x-ray done- they can tell if there are any bone spurs or loss in disk height.
- An MRI for spinal stenosis is a gold standard tool- to see how the nerves, disks and the spinal cord are working. They can also check for tumours which may otherwise be difficult to visualise.
- A CT scan may be done using a contrast dye- so that clearer images of the nerves and spinal cord can be taken for diagnosis.
Treatment of Spinal Stenosis
There are both non-surgical treatment options and surgical approaches that are possible. It all depends on the severity of your symptoms, where the issue is along the spine and how much your daily quality of life is getting affected because of pain, stiffness or neuropathy. Some conventional methods to try include
Heat or cold therapy- heat is good to increase blood flow while ice can help reduce inflammation. Exercise is a fool proof way to feel better, but you need to follow the right technique. You may be given painkillers or steroid injections to deal with your pain.
If none of these work, then you may need surgery. Spine decompression surgery is a very common procedure that involves the removal of bone spurs and some part of the vertebrae- to make more room for the nerves. Either the full lamina or parts of it are removed. Some other procedures include- removing the vertebral bone that is compressing the nerve roots at the foramen. A spinal fusion is suggested in extreme cases but cannot be reversed afterwards. This permanent procedure is done to fuse the affected vertebrae.
If spinal stenosis is not treated on time, it can cause unwanted complications like loss of bladder control or some form of sexual dysfunction. In extreme cases, even leg paralysis has been observed.
Conclusion
Spinal stenosis is a chronic condition that cannot be completely prevented. You can however learn to eat better, exercise well and regularly and ensure that your bones stay healthy. You can opt to take supplements if you are not sure of getting all nutrients from your meals alone, but talking to a doctor before doing that is always best. Practicing good posture, not smoking and trying to maintain a healthy body weight can reduce undue stress on your nerves and joints too. If there is any pain or symptoms that you are worried about, call us for a consultation today!